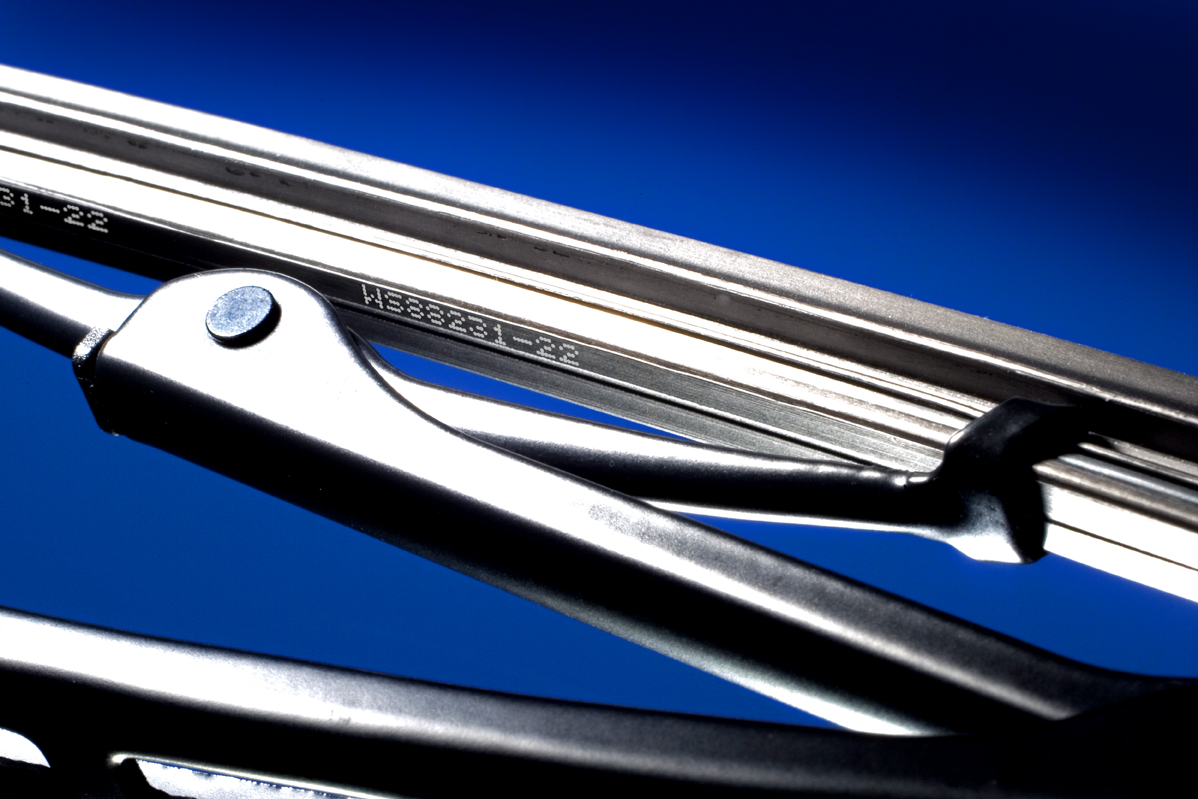
CODING AND MARKING SOLUTIONS FOR AUTOMOTIVE MANUFACTURING
Quick Links:
Introduction
The ongoing emergence of the electric car, the self-driving car, and the connected car – as well as the growing trend of ride-sharing – all point to a future for the automotive industry that will look very different to the present.
But while we may be on the cusp of a revolution in the way we travel, one thing remains constant: the automotive manufacturer’s need for clear and traceable batch coding solutions.
In the US, the automotive industry remains a vital part of the economy and America’s job growth. Additionally, with new tariff legislation on imported goods, American manufacturers are increasingly turning to American-made parts.
It is against that background that the key importance of robust coding, for traceability and supply chain management, becomes clear. With a modern vehicle containing thousands of individual components, many needing to carry a specific part number, there is no room for error in the selection of coding and marking equipment.
From suppliers manufacturing the smallest parts, to vehicle makers relying on the correct coding for traceability through the assembly process and beyond, the inclusion of information which stays in place – whether on metal, rubber, plastic, glass, fabric or card – is a crucial part of the process.

With some manufacturers continuing to recall their products, it is particularly important that traceability codes are clear and robust. The problem of a defective part is a massive one for any vehicle manufacturer, but it is made more manageable by effective coding.
Even more pressing than recalls is the need to combat counterfeiting. Fakes, including counterfeit brake pads, tires, suspension components, steering linkages and other accessories, are being distributed and sold to consumers in ever-greater volumes around the world.
In recent times, we have seen police collaborating with motor industry experts to tackle car part counterfeiting, as well as a leading car manufacturer undertaking legal proceedings against a major internet retailer over alleged sales of counterfeit vehicle parts.
See Daimler hits Amazon with new lawsuit over ‘counterfeit’ auto parts
It is estimated that the total economic and social costs globally due to counterfeiting and piracy worldwide, which stood at $737-898bn in 2013, will rise to $1.54-1.87trn by 2022 – a worrying suggestion that the problem of counterfeit automotive goods will only get worse.
See Hologram body says counterfeit impact on jobs ‘disturbing’
Brand protection
High resolution, long-lasting product codes for direct parts marking and unique identification will ensure that automotive products satisfy necessary legislation and customer requirements, with regard to clear, durable codes that stay in place during the lifetime of the component.
Counterfeiting can be combated by printing legibly and durably onto products. The latest inks offer a number of benefits that provide effective protection against counterfeiting, such as high contrast on a range of substrates including dark surfaces, PVC, rubber, glass, and electronic components, and resistance to acids, alkalis, and high levels of light or heat (making them resistant to code transfer during handling and cable-winding, for example).
In addition, the ability to print company logos, Data Matrix codes and scannable barcodes provides manufacturers with traceability codes in a secure format on their products. This also reassures end customers and resellers that the product is genuine.
Quality
Less downtime on your production line means reduced cost to your business. Also, by providing correctly coded components to your customers, they will benefit from less downtime on their own production lines, meaning less chance of you losing their business.
High quality printers ensure consistent and reliable coding, with long service intervals and low-cost maintenance to maximise production performance while minimising operating costs.
Robust printers will be able to operate continually even in 24/7 production environments. Printers with IP55 or IP65-rated steel enclosures, or a sealed printhead, offer protection against liquid or particle contamination, and can operate in dusty or wet environments to prevent unplanned stoppages.
Tough yet flexible printhead conduits can cope with repetitive actions such as traversing applications, and contribute towards continual operation.
Quality machines will also offer greater functionality, helping to reduce costs while maximising efficiencies. For example, printers with a carton coding feature have the flexibility to code both primary and secondary packaging with a single machine.
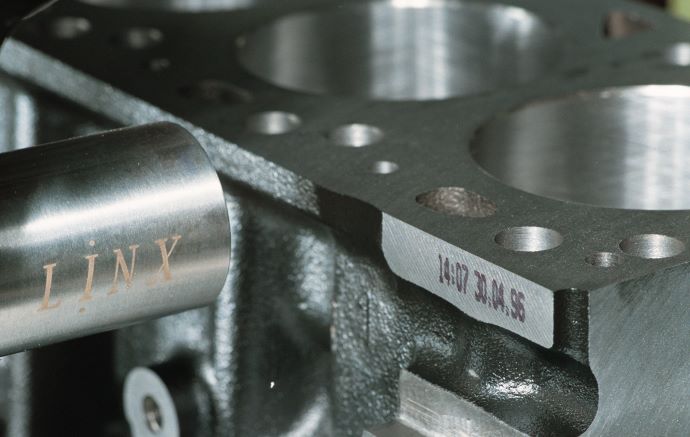

Productivity
Printing and marking systems can help to minimise product waste, reduce code errors and rework, and therefore increase manufacturing uptime.
Increased speed and flexibility
Traversing printheads are able to code across multiple products at high speeds. Versatile printers that can handle a variety of requirements, including multiple lines of text, and human- and machine-readable codes, will enable manufacturers to meet differing standards or regulations.
Reducing stoppages
Features such as self-cleaning printheads will reduce blocked nozzles and maximize printer uptime, while timely and visible notifications of low fluid levels allow refills to be scheduled into planned production line stops.
Planned stoppages can also be minimised through the use of printers with longer service intervals. Ink jet printers with pigmented inks provide a dense, clear code, but due to the nature of the inks you need to check the service intervals for the printers – some suppliers will offer much longer service intervals meaning less frequent downtime for cleaning.
In addition, self-servicing and self-maintenance functions allow operators to fit maintenance in around their own schedules, meaning more efficient operations Machines designed for use in washdown environments save time covering or removing them for cleaning.
Reducing waiting time
For manufacturers needing regular product changeovers, digital printing and marking technology allows multiple messages to be stored. These can then be switched at the press of a button, reducing the time spent setting up new information compared to changing rollers or plates on non-digital machines.This is particularly useful for contract manufacturers who may produce thousands of SKUs for different customers, with frequent message changeovers required. Quick changeovers are essential to reduce waiting time between product runs.
Multiple line settings as well as data held in the printer’s memory mean information specific to product lines can be set up and indexed in the machine, making for quick product changeovers.
Lightweight machines that can be moved between lines and set up quickly reduce set-up time and downtime between production runs. They also allow producers to react quickly to changes in customer orders and to be more flexible in their operations.

Reducing waste
The best printing and marking solutions help to minimise waste by ensuring the correct information is printed every time, that it is legible and in the right place on the product.
One way they achieve this is through simple message selection, intuitive user interfaces, and large message storage capacities, which help ensure the right code is selected first time, every time. Automated message selection and remote monitoring further reduce the risk of code errors.
Reducing processes and over-production
Technology which requires minimal start-up procedures and where the first print is as good as the last means there is no need to leave machines switched on permanently, or to run them every day.
Machine versatility, such as the ability to print multiple lines of variable information as well as logos and carton coding all with one printer, will enable manufacturers to use a single model for several applications, printing onto a range of substrates. Less variation in machine types also leads to fewer instructions to learn and a reduced inventory of consumables.
Printer selection – factors to consider
Linx’s own Voice of Customer research suggests that the key drivers behind printer purchases in the automotive industry include reliability in helping to meet production targets; accurate printing of right-first-time codes onto a range of surfaces, avoiding reworks; and legible, durable codes that can combat counterfeiters.
As part of the selection process, the speed of the line and the substrates to be printed onto are critical. It is important to have each material type sample-printed to ensure legibility, particularly if a range of different colours is involved. Consider also a trial of a printer on the production line, so that it is exposed to real-life environments and processes.
The overall Cost of Ownership of any new machine purchase should be investigated. This takes into account both the initial price and factors such as reliability and the cost of consumables over the machine’s lifetime, plus the cost and frequency of servicing the printer. Frequent breakdowns can negate any benefits of a lower purchase price. Leasing and rental options may also be worth exploring.
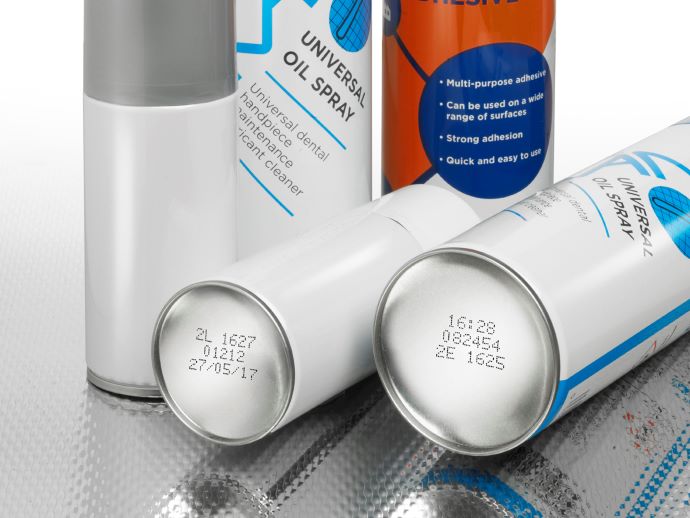

The different coding technologies
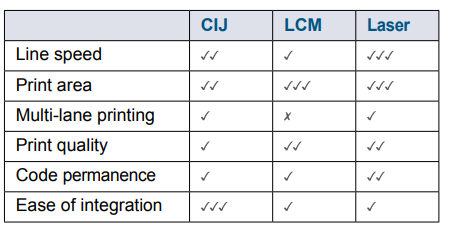
Continuous Ink Jet (CIJ)
A non-contact printing technology, CIJ has the ability to print onto almost any substrate. A wide range of inks is available, including pigmented inks of different colours which provide excellent code contrast on dark components such as rubber hoses, mountings, and trim.
Fast-drying inks and UV cure inks provide premium adhesion and light fastness, as well as resistance to a range of chemicals, so are suitable for components within the engine bay itself or where they may be exposed to chemicals such as brake fluid or oil. Fast-drying inks are widely used in cable marking applications where they prevent code transference during production processes such as cable-winding.
CIJ can print from one to multiple lines of text and simple graphics on line speeds of over 23ft/s for a single line of code. The compact printhead can be situated above, beside or beneath a production line or traverse from side to side across the line. With lighter models increasingly being produced, the CIJ printer is more capable of being quickly moved from line to line and is fast to install and set up. The technology can provide the ideal solution to enable start-up and growing businesses to move from manual coding to digital printing methods in order to produce higher quality and greater consistency of codes.
Large Character Marking (LCM)
Case coders are particularly well-suited for printing variable information onto secondary packaging such as cardboard boxes. These outer cases usually require text and graphics which are easy to see.
Case coders can print to a high-resolution quality, and are versatile enough for use on a variety of surfaces and materials. Benefits include ease of set-up and adjustment, reliability and predictable cost of ownership. They are a cost-effective alternative to pre-printed boxes or labels.
Thermal Ink Jet Printers (TIJ)
TIJ printers provide a flexible printed coding solution for both outer cases and primary packaging.
Although having a smaller print area than case coders, their high resolution offers superb print quality for premium packaging, making them a cost-effective solution for slower production lines or where production is not 24/7.
Laser
Laser marking provides a permanent, hiqh quality code onto a wide range of substrates including EDPM rubber weather strips, glass and plastic, and at high line speeds. Benefits include increased uptime, higher speed capability and the fact there is no use of consumables.
Modern, steered beam laser systems are highly versatile as they provide clear, consistent and perfectly formed characters in a variety of fonts and message formats, and enable the use of high quality graphics and logos over relatively large print areas.
They are particularly effective for graphics, logos and 2D Data Matrix codes, which support anti-counterfeiting measures.
Fiber laser marking technology offers marking on the widest range of materials, including bare metal, such as: under-trays; engine blocks; bearings; VIN plates; coated and bare aluminium components; and rubber profiles. Oil and other chemical containers made from HDPE can also be permanently marked with fiber laser. The fine spot size allows printing of a large amount of information in a small area, as well as marking very small components such as fuel lines.
As laser coders can cover a large print area and on high line speeds, they are suitable for multi-lane printing onto multiple products in one pass, without the need for a mechanical moving printhead.
Advances in technology and efficiency have led to a significant reduction in the initial purchase price, and laser coders deliver low cost of ownership due to no consumables and relatively low maintenance.
Compact supply units and marking heads enable easy integration into existing production lines or static coding applications, with minimum disruption to workflows.

Conclusion
In an industry which requires information to be printed onto individual components at various stages of the process, coding and marking equipment must be able to meet complex demands comfortably.
Robust coders are required to operate reliably in challenging production environments, with trouble-free integration into production processes.
Code functions vary in the industry: codes may need to be removable for internal traceability; discreet for anti-counterfeiting purposes; or long-lasting to meet customer traceability requirements.
An effective coding solution, tailored to the manufacturer’s requirements, can help facilitate smooth manufacturing and assembly processes, as well as helping vehicle manufacturers deliver top-quality after-care.

